Step Tracker Key Features
1. Full-Stack Implementation
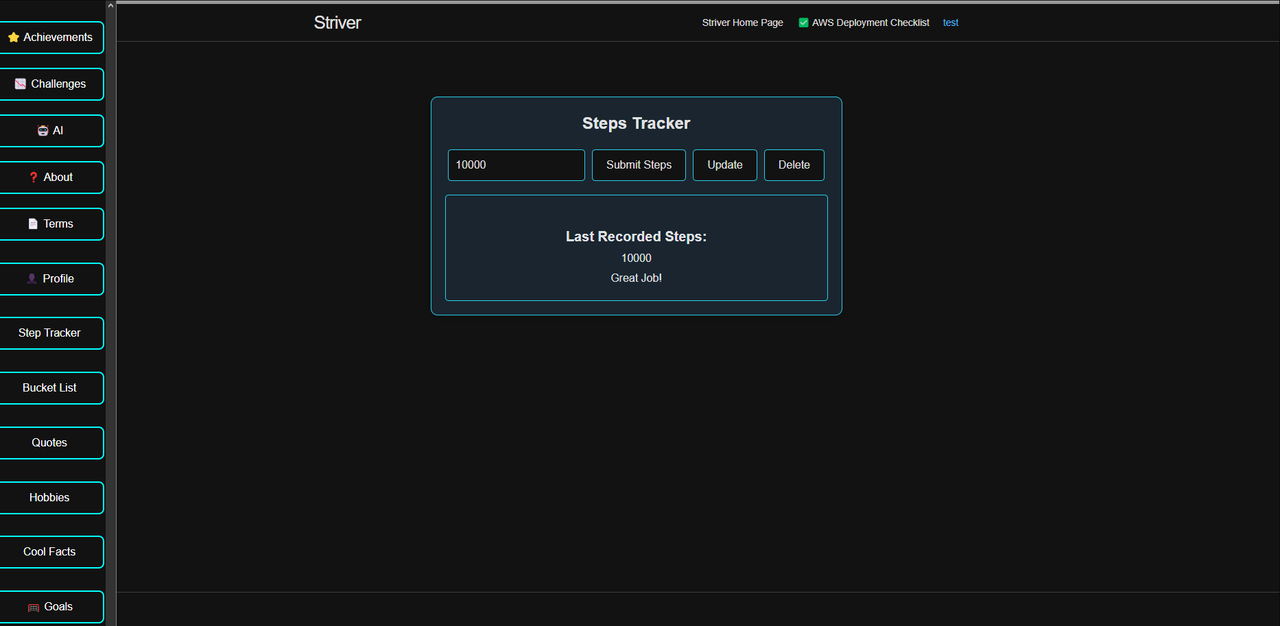
- The Step Tracker feature integrates frontend, backend, and a database
- Uses Flask (Python) for backend API handling.
- Uses JavaScript for frontend interaction.
- Stores data in a database using SQLAlchemy.
CPT Requirements
| Requirement | A database | A procedure | A call to the procedure | Selection | Iteration | Sequencing | Input From User |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Tracker | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
- Database
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
db = SQLAlchemy()
class Steps(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'steps'
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
user = db.Column(db.String(255), nullable=False)
steps = db.Column(db.Integer, nullable=False)
def create(self):
db.session.add(self)
db.session.commit()
This creates the database table
- A procedure
def add_step_entry(user, step_count):
new_entry = Steps(user=user, steps=step_count)
new_entry.create()
- Creates a new step entry
-
Saves the entry into the database
- A call to a procedure
@app.route('/api/add_steps', methods=['POST'])
def handle_add_steps():
data = request.get_json()
user = data.get('user')
steps = data.get('steps')
add_step_entry(user, steps)
return jsonify({'message': 'Steps added successfully'})
The backend listens at /api/add_steps, grabs the JSON data (username + steps), and calls add_step_entry() to save it in the database.
- Selection
def validate_steps(steps):
if steps is None or not isinstance(steps, int) or steps < 0:
return "Invalid step count"
else:
return "Valid step count"
This ensures the input is a valid, non-negative whole number before processing.
- Iteration
@staticmethod
def restore(data):
with app.app_context():
db.session.query(Steps).delete()
db.session.commit()
for steps_data in data:
steps = Steps(user=steps_data['user'], steps=steps_data['steps'])
steps.create()
This function deletes all existing step data and then iterates through a list of new entries, adding them to the database one by one.
- Sequencing
def process_step_entry(user, steps):
validated = validate_steps(steps)
if validated == "Valid step count":
add_step_entry(user, steps)
print("Step entry added!")
This function validates the step count, ensures it is correct, and then calls add_step_entry() to store it in the database
- Input from User
<input type="number" id="steps-input" placeholder="Enter steps">
<button onclick="submitSteps()">Submit Steps</button>
async function submitSteps() {
const steps = parseInt(document.getElementById('steps-input').value, 10);
if (isNaN(steps) || steps <= 0) {
alert("Please enter a valid number of steps");
return;
}
await fetch('/api/steps', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ steps }),
credentials: 'include'
});
alert("Steps submitted successfully!");
}
This function takes the user’s input, checks if it’s a valid number, and then submits it to the backend for processing